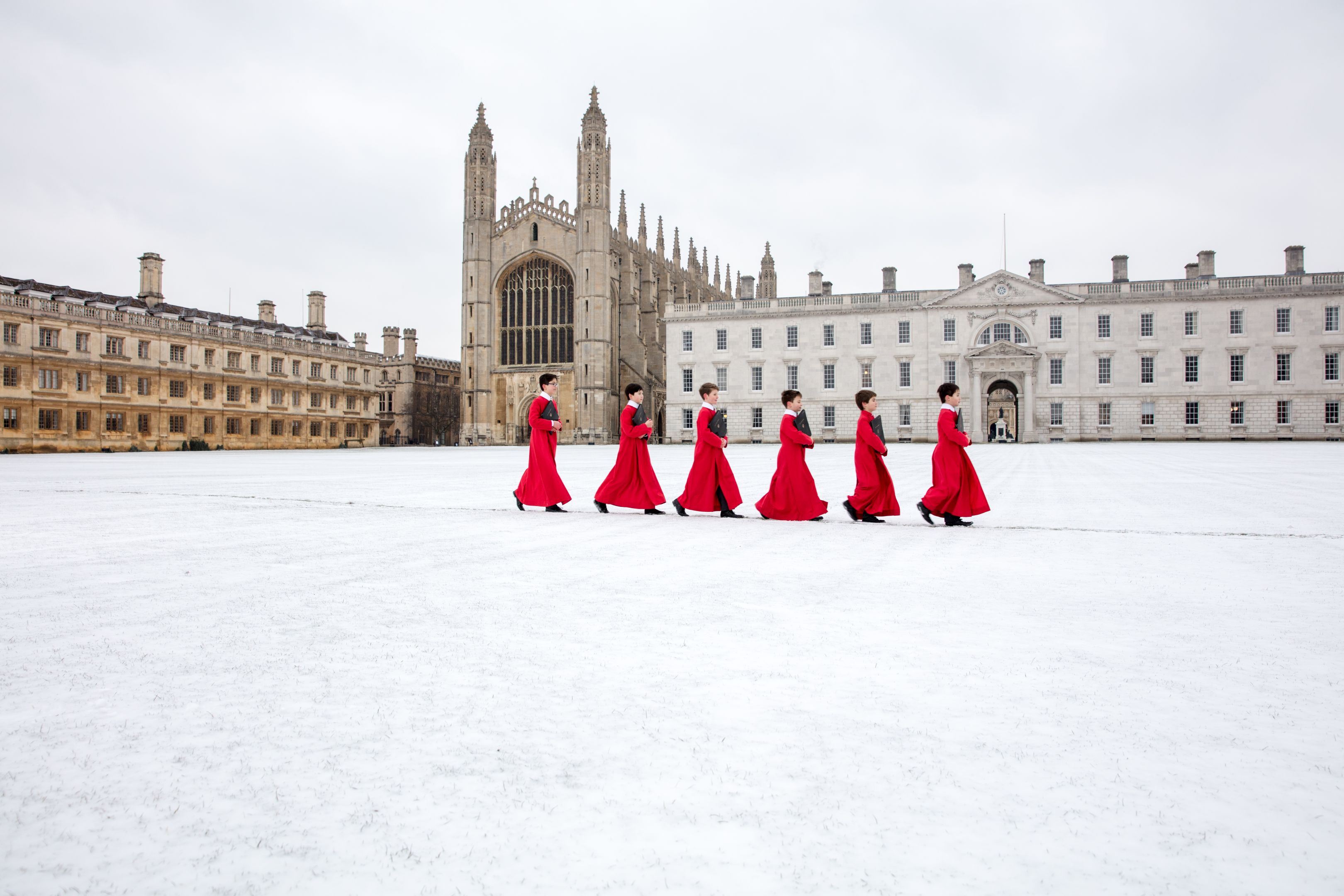
A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols
A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols is the Christmas Eve service held in King's College Chapel since 1918. It was first broadcast in 1928 and is now broadcast to millions of people.
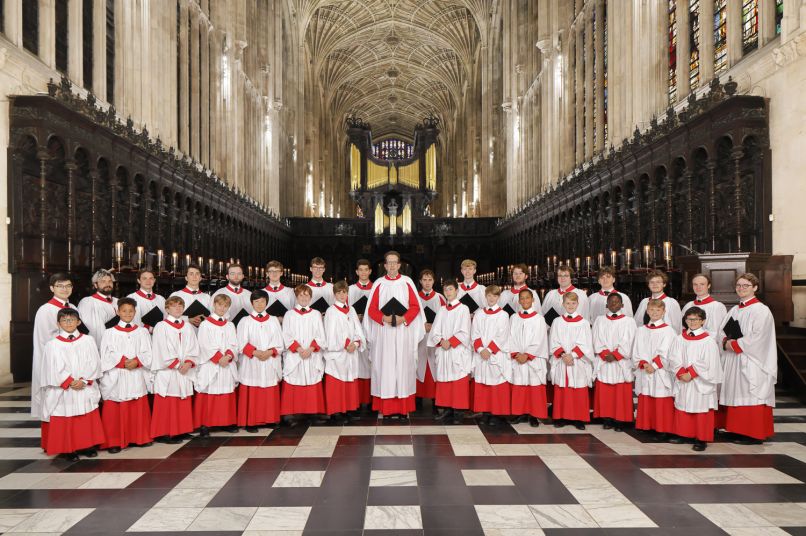

A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols was introduced by Eric Milner-White in 1918 to bring a more imaginative approach to worship. The service includes readings from the Bible. The opening carol is always 'Once in Royal David's City', and there is always a new, specially commissioned carol.
It is distinct from Carols from King's, which is a carol service pre-recorded for BBC television, also broadcast on Christmas Eve.
Attending A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols
A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols was first conceived as a gift to the City of Cambridge and it is in that spirit that the College makes approximately half the tickets for this service available to members of the public. Tickets are distributed in advance to those who are successful in the annual online ballot. There is no longer a public queue for tickets.
There are two online ballots: one for those applying from overseas (to allow time for long-distance travel arrangements to be made), and one main ballot for UK residents and those from overseas who do not apply in the earlier ballot. If you are a UK resident, please do not attempt to apply using the overseas form because your application will be discounted. Please use the links below to access the forms and note the opening and closing dates. The forms will only accept responses during these times.
Overseas ballot application form
The overseas ballot for tickets opens on Wednesday 1 October at 9.00am and closes on Wednesday 15 October at 5.00pm. Successful applicants will be notified by Friday 7 November. We are only able to contact those who are successful.
Main (UK) ballot application form
The main ballot for tickets opens on Saturday 1 November at 9.00am and closes on Saturday 15 November at 5.00pm. Successful applicants will be notified by Friday 5 December. We are only able to contact those who are successful.
If you are unable to use the online forms to apply, ballot entry can be made by writing to the Dean by post. If you write you should include an email address, or, if you do not have an email address, a stamped addressed envelope. Please bear in mind that this process simply means that your name will be entered manually into the same ballot as online applications, so do consider applying using the above forms unless you are unable to do so.
Each application may be for one or two tickets only and must:
- include the name of both people who wish to attend;
- include an email address and phone number;
- be submitted by 5.00pm on the stated deadline.
PLEASE NOTE this service is not suitable for very young children and babies or those who may find it difficult to remain quiet for the duration of the service.
While A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols is intended as a gift to the city of Cambridge, the Advent Procession on Sunday 30 November 2025 is primarily a College occasion. However, we are making a number of tickets available on a 'first come, first served' basis to members of the Cambridge University community and the wider public. Admission is by ticket only and you may apply for up to two tickets using the link below.
Advent Procession application form
Applications must be submitted by 9.00am on Monday 17 November. We will write to you before Tuesday 25 November to indicate whether or not we can fulfil your request.
Listening to the service
A Festival of Nine Lessons and Carols is broadcast live on BBC Radio 4 and the BBC World Service on 24 December at 3pm GMT (10:00 EST or 07:00 PST). The service is also re-broadcast at 1pm on Radio 3 on Christmas Day, and at various times on the BBC World Service.
In the United States the service is distributed by American Public Media and is broadcast by over 400 radio stations, including Minnesota Public Radio and WQXR in New York. As there is no list of radio stations that are broadcasting the service it's best to contact your local stations or check their online listings.


